Q: How can I make the most of my manager's feedback?
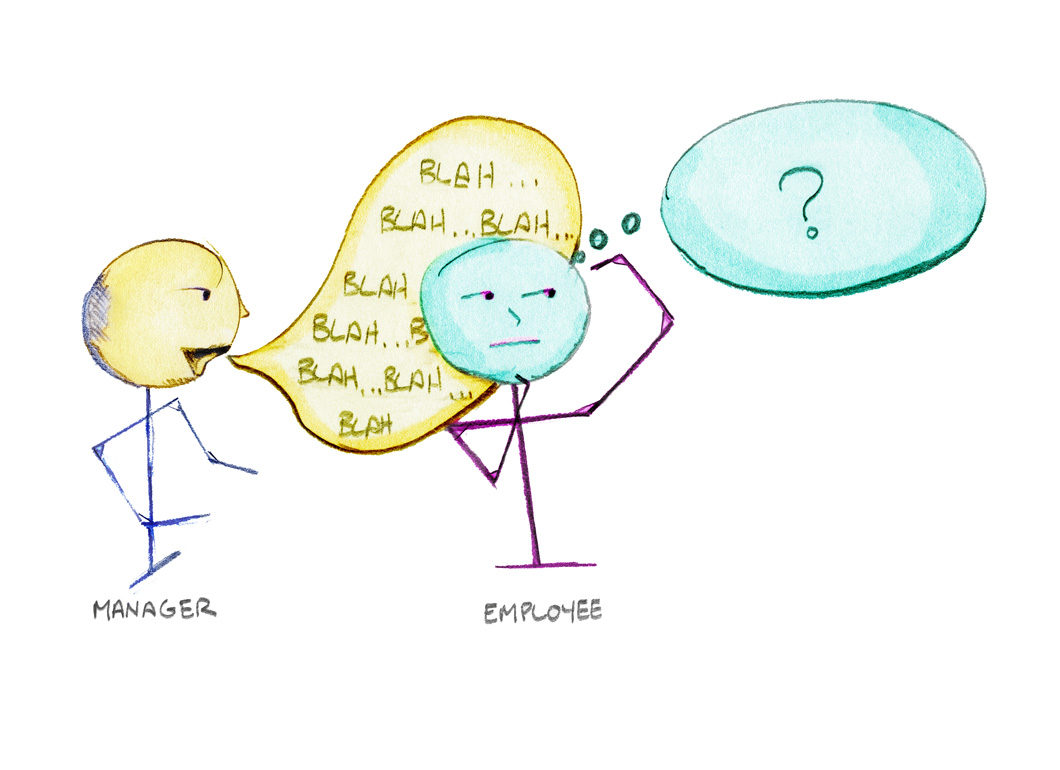
“I recently had a performance review with my manager and it didn’t feel particularly useful. I could tell he received some feedback and was just repeating it. I argued my points and yeah now what?! I get that I own 50% of the communication problem, so what should I be doing to better receive feedback?”
A:
People fear judgement
Forget what you may have been told
This is why we are told to lace feedback with positive observations. The hope is that some how people won’t feel as bad with the real feedback, because it isn’t all bad news. These old school techniques help deliver the message, and the problem remains. The person hearing the feedback is not open to receiving, because it feels disingenuous.
Seeking out feedback
Getting better at receiving feedback
So, how do we get better at receiving feedback?
- People do not provide feedback enough. Feedback should happen so often that no one is ever surprised finding out too late. Receiving feedback gets better as you learn how to thoughtfully give it.
- When we provide feedback, we don’t spend the time to consider the individual’s a) response b) context c) next steps. There is a level of empathy needed to consider not just the message, but how the content will be and should be received.
If someone feels the need to provide feedback, take the opportunity to process it. We can always decide to discard it later, but if we don’t hear it and process it, we won’t know if there is something there to work on.
Three steps to better reception
- Listen. We are all too quick to respond with the reasons why we care the way we are. As if we may lose the opportunity to defend ourselves. So, listen to what is being said to effectively make sense of the feedback.
- Process. Active listening means you need to be able to repeat what you heard in your own words, to verify and communicate your understanding. Ask yourself: What is being said? Can you repeat back in your own words what was said? Are there specific examples that can help you synthesize a pattern of understanding the content and the impact it is having?
- Evaluate. No one expects change to happen upon awareness. At least not unless it’s a severe issue needing immediate change, such as in the cases of violations of code of conduct, safety or law. Assuming we are working with typical feedback, the kind intended to make us better, it needs to be sorted and evaluated.
First, is it true? If it is true, then what needs to change to address the feedback? Behavior, skill or experience. A plan of action is required to make any meaningful change.
Example Feedback
Example Action
For every meeting, begin by writing a simple intention at the top of your notes.
For some this may read too “out there,” but honestly, intention matters. Consistently set the kind of intention you want and you will change the behavior.
Next steps: Actions that change everything
2 Steps to Receiving Feedback Better
- Seek out feedback from others.
- Listen, process and evaluate in that order.
6 Steps to Providing Feedback
- Consider feedback that needs to be delivered.
- Capture notes focus on the facts, a timely example and the impact.
- Understand the individual’s context.
- Create a safe environment for providing the feedback.
- Ask to provide feedback when you have it.
- Deliver the feedback focusing on the notes you created vs. off-the-cuff.
If you are a manager, be sure to check out the related post:
Three tools for all leaders
READ
Judgment Detox: Release the Beliefs That Hold You Back from Living A Better Life
by Gabrielle Bernstein
READ
The 7 Habits of Highly Effective People: Powerful Lessons in Personal Change
by Stephen R. Covey
We use affiliate links on this site. We make a bit of money when you click on those links. It costs you nothing and helps us spread the word.